Structures of oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS)
Polyhedral Silsesquioxanes
Research on compounds containing the Si–O bond has for years been dominated by
silicon dioxide, minerals containing repeating SiO₂ fragments, and silicones
composed of repeating R₂SiO units (R = alkyl or phenyl). Over the past 20–30
years, there has been a noticeable increase in studies on silsesquioxanes
containing the RSiO₁.₅ unit. These compounds, due to the presence of both an
inorganic fragment and an organic group, possess hybrid properties. The
inorganic Si–O–Si fragment imparts chemical and thermal resistance to these
compounds, while the organic R group increases their solubility and provides
appropriate reactivity. A wide range of polymeric structures with the general
formula (RSiO₁.₅)ₙ can be synthesized, but the most interesting are those with
polyhedral architectures.⁴
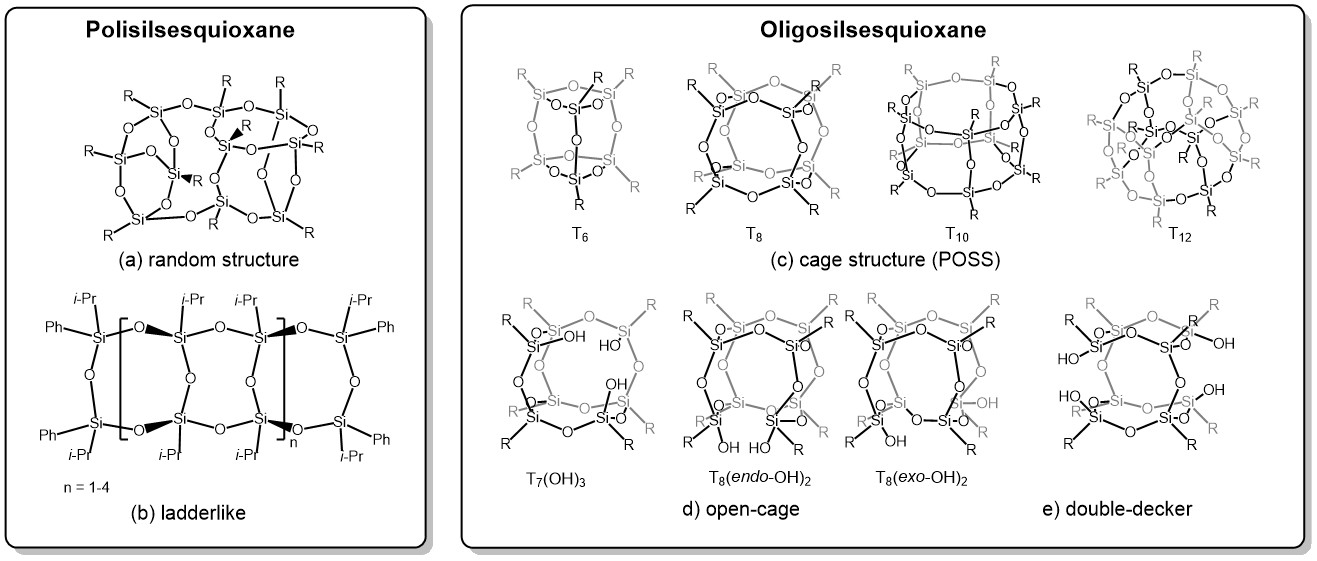
Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS) are
three-dimensional organosilicon compounds with the general empirical formula
(RSiO₁.₅)ₙ (where R = H, alkyl, alkenyl, or aryl; n = 6, 8, 10, 12). A wide
variety of POSS structures can be obtained, such as ladder-like (Figure 3, part
b), cage-like structures differing in the number of silicon atoms (Figure 3,
part c), and open cages (Figure 3, parts d–f). Polyhedral silsesquioxanes
exhibit high chemical and thermal resistance,⁵–¹¹ making them useful precursors
for the production of functional materials such as porous materials,¹²–¹⁸
catalysts,¹⁹–²¹ superhydrophobic materials,²²-³³ luminescent materials,³⁴-⁴²
composites,⁴³–⁵² and others.⁵³
Through appropriate modification of POSS side
groups, it is possible to "tune" their solubility, which allows for
the preparation of soluble silsesquioxane nanoparticles with sizes up to 5
nm.⁵⁴,⁵⁵ In contrast to organosilicon materials obtained via the sol–gel
method—which in most cases exhibit undefined structures (Figure 3, part a)—the
use of polyhedral silsesquioxanes allows for better control over the structure
and morphology of the resulting nanoparticles. Due to their well-defined three-dimensional
architecture, the most interesting group of silsesquioxanes are the cage-type
compounds (Figure 3, part c). It is possible to obtain cages of various
geometries and sizes, such as octamers, decamers, or dodecamers (denoted as T8,
T10, T12). Their unique properties are related to their
three-dimensional core and nanometric size, which allows for the emergence of
properties not observed at the macroscale.⁴
Nomenclature and Designations
The English term silsesquioxane derives from Latin and can be interpreted as follows: silicium (silicon), sesqui (one and a half), oxygenium (oxygen), indicating that the ratio of oxygen atoms to silicon atoms is 1.5.⁵⁶ In Polish-language literature, the term is commonly adapted as silseskwioksan. The use of systematic names for polyhedral silsesquioxanes can be cumbersome; therefore, the nomenclature typically used for siloxanes is often applied.⁵⁷ This classification distinguishes five types of silicon atoms (Figure 4). The "M" type denotes a silicon atom bonded to three organic groups and one oxygen atom. A "D"-type silicon atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms, a "T"-type to three oxygen atoms, and a "Q"-type to four oxygen atoms.⁵⁶
Si–O bonds can form either siloxane groups (Si–O–Si) or silanol groups (Si–OH). To distinguish between them, a superscript is used to indicate the number of Si–O–Si connections formed by a silicon atom. For example, T³ denotes a silicon atom bonded to one organic group and three siloxane linkages. Polyhedral silsesquioxanes contain T³-type silicon atoms. The number of silicon atoms is given as a subscript. The designation T₈R₈ or R₈T₈ refers to an octameric hexahedral silsesquioxane containing eight organic side groups or hydrogen atoms. The formula Me₈T₈ corresponds to octamethyl-octasilsesquioxane, a compound with the systematic name octamethyl-pentacyclo[9.5.1.1³,⁹.1⁵,¹⁵.1⁷,¹³]octasiloxane, shown in Figure 5.
The material presented in this dissertation has been or will be published in English. Therefore, the consistent use of the English number format (with a period as the decimal separator) was adopted, which is especially convenient in the context of NMR spectra interpretation.
Figure 5. Structure of octamethyl-octasilsesquioxane (Me₈T₈).(4) Cordes,
D. B.; Lickiss, P. D.; Rataboul, F. Recent Developments in the Chemistry of
Cubic Polyhedral Oligosilsesquioxanes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110
(4), 2081–2173. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900201r.
(5) Rücker,
C.; Kümmerer, K. Environmental Chemistry of Organosiloxanes. Chem. Rev. 2015,
115 (1), 466–524. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500319v.
(6) Fina,
A.; Tabuani, D.; Carniato, F.; Frache, A.; Boccaleri, E.; Camino, G. Polyhedral
Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes (POSS) Thermal Degradation. Thermochim. Acta 2006,
440 (1), 36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2005.10.006.
(7) Han,
Z.; Xi, Y.; Kwon, Y. Thermal Stability and Ablation Behavior of Modified
Polydimethylsiloxane-Based Polyurethane Composites Reinforced with Polyhedral
Oligomeric Silsesquioxane. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16
(2), 1928–1933.
(8) Barczewski,
M.; Chmielewska, D.; Dobrzyńska-Mizera, M.; Dudziec, B.; Sterzyński, T. Thermal
Stability and Flammability of Polypropylene-Silsesquioxane Nanocomposites. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2014, 19 (6),
500–509. https://doi.org/10.1080/1023666X.2014.922268.
(9) Qian, Y.; Wei, P.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, P.;
Yu, H. Flame Retardancy and Thermal Stability of Polyhedral Oligomeric
Silsesquioxane Nanocomposites. Fire Mater. 2013, 37 (1),
1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.1126.
(10) Chen, S.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.
Intumescent Flame-Retardant and Self-Healing Superhydrophobic Coatings on
Cotton Fabric. ACS Nano 2015, 9 (4), 4070–4076.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b00121.
(11) Zucchi, I. A.; Galante, M. J.; Williams, R.
J. J.; Franchini, E.; Galy, J.; Gérard, J.-F. Monofunctional Epoxy-POSS
Dispersed in Epoxy−Amine Networks: Effect of a Prereaction on the Morphology
and Crystallinity of POSS Domains. Macromolecules 2007, 40
(4), 1274–1282. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma062188y.
(12) Xing, Y.; Peng, J.; Xu, K.; Lin, W.; Gao,
S.; Ren, Y.; Gui, X.; Liang, S.; Chen, M. Polymerizable Molecular
Silsesquioxane Cage Armored Hybrid Microcapsules with In Situ Shell
Functionalization. Chem. – Eur. J. 2016, 22 (6),
2114–2126. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201504473.
(13) Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Qian, Z.; Guo, J.;
Dong, H.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Robust Superhydrophobic Bridged Silsesquioxane
Aerogels with Tunable Performances and Their Applications. ACS Appl. Mater.
Interfaces 2015, 7 (3), 2016–2024.
https://doi.org/10.1021/am5077765.
(14) Alves, F.; Scholder, P.; Nischang, I.
Conceptual Design of Large Surface Area Porous Polymeric Hybrid Media Based on
Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Precursors: Preparation, Tailoring of
Porous Properties, and Internal Surface Functionalization. ACS Appl. Mater.
Interfaces 2013, 5 (7), 2517–2526.
https://doi.org/10.1021/am303048y.
(15) Guo, H.; Meador, M. A. B.; McCorkle, L.;
Quade, D. J.; Guo, J.; Hamilton, B.; Cakmak, M.; Sprowl, G. Polyimide Aerogels
Cross-Linked through Amine Functionalized Polyoligomeric Silsesquioxane. ACS
Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3 (2), 546–552.
https://doi.org/10.1021/am101123h.
(16) Lee, J. H.; Lee, A. S.; Lee, J.-C.; Hong,
S. M.; Hwang, S. S.; Koo, C. M. Multifunctional Mesoporous Ionic Gels and
Scaffolds Derived from Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes. ACS Appl.
Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9 (4), 3616–3623.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12340.
(17) Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.;
Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. Superhydrophilic Antireflective Periodic Mesoporous
Organosilica Coating on Flexible Polyimide Substrate with Strong
Abrasion-Resistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9
(6), 5468–5476. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b14117.
(18) Sangtrirutnugul, P.; Chaiprasert, T.;
Hunsiri, W.; Jitjaroendee, T.; Songkhum, P.; Laohhasurayotin, K.; Osotchan, T.;
Ervithayasuporn, V. Tunable Porosity of Crosslinked-Polyhedral Oligomeric
Silsesquioxane (POSS) Supports for Palladium-Catalyzed Aerobic Alcohol
Oxidation in Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9
(14), 12812–12822. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b03910.
(19) Rozanska, X.; Fortrie, R.; Sauer, J.
Size-Dependent Catalytic Activity of Supported Vanadium Oxide Species:
Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Propane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136
(21), 7751–7761. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja503130z.
(20) Quadrelli, E. A.; Basset, J.-M. On
Silsesquioxanes’ Accuracy as Molecular Models for Silica-Grafted Complexes in
Heterogeneous Catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254
(5–6), 707–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.09.031.
(21) Mohapatra, S.; Chaiprasert, T.;
Sodkhomkhum, R.; Kunthom, R.; Hanprasit, S.; Sangtrirutnugul, P.;
Ervithayasuporn, V. Solid-State Synthesis of Polyhedral Oligomeric
Silsesquioxane-Supported N-Heterocyclic Carbenes/Imidazolium Salts on Palladium
Nanoparticles: Highly Active and Recyclable Catalyst. ChemistrySelect 2016,
1 (16), 5353–5357. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201600878.
(22) Wang, H.; Xue, Y.; Ding, J.; Feng, L.;
Wang, X.; Lin, T. Durable, Self-Healing Superhydrophobic and Superoleophobic
Surfaces from Fluorinated-Decyl Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane and
Hydrolyzed Fluorinated Alkyl Silane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50
(48), 11433–11436. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201105069.
(23) Chinnam, P. R.; Wunder, S. L.
Polyoctahedral Silsesquioxane-Nanoparticle Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries:
POSS-Lithium Salts and POSS-PEGs. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23
(23), 5111–5121. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm2015675.
(24) Douvas, A. M.; Van Roey, F.; Goethals, M.;
Papadokostaki, K. G.; Yannakopoulou, K.; Niakoula, D.; Gogolides, E.; Argitis,
P. Partially Fluorinated, Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane-Functionalized
(Meth)Acrylate Resists for 193 Nm Bilayer Lithography. Chem. Mater. 2006,
18 (17), 4040–4048. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0605522.
(25) Yang, S.; Mirau, P. A.; Pai, C.-S.;
Nalamasu, O.; Reichmanis, E.; Lin, E. K.; Lee, H.-J.; Gidley, D. W.; Sun, J.
Molecular Templating of Nanoporous Ultralow Dielectric Constant (≈1.5)
Organosilicates by Tailoring the Microphase Separation of Triblock Copolymers. Chem.
Mater. 2001, 13 (9), 2762–2764.
https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0102786.
(26) Romeo, H. E.; Fanovich, M. A.; Williams, R.
J. J.; Matějka, L.; Pleštil, J.; Brus, J. Self-Assembly of a Bridged
Silsesquioxane Containing a Pendant Hydrophobic Chain in the Organic Bridge. Macromolecules
2007, 40 (5), 1435–1443. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma062091b.
(27) Yue, K.; Liu, C.; Guo, K.; Yu, X.; Huang,
M.; Li, Y.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Cheng, S. Z. D.; Zhang, W.-B. Sequential “Click”
Approach to Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane-Based Shape Amphiphiles. Macromolecules
2012, 45 (20), 8126–8134. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma3013256.
(28) Dopierała, K.; Bojakowska, K.; Karasiewicz,
J.; Maciejewski, H.; Prochaska, K. Interfacial Behaviour of Cubic
Silsesquioxane and Silica Nanoparticles in Langmuir and Langmuir–Blodgett
Films. RSC Adv. 2016, 6 (97), 94934–94941.
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA18255K.
(29) Iacono, S. T.; Vij, A.; Grabow, W.; Smith,
Jr., D. W.; Mabry, J. M. Facile Synthesis of Hydrophobic Fluoroalkyl
Functionalized Silsesquioxane Nanostructures. Chem. Commun. 2007,
No. 47, 4992–4994. https://doi.org/10.1039/b712976a.
(30) Kapoor, M. P.; Sinha, A. K.; Seelan, S.;
Inagaki, S.; Tsubota, S.; Yoshida, H.; Haruta, M. Hydrophobicity Induced
Vapor-Phase Oxidation of Propene over Gold Supported on Titanium Incorporated
Hybrid Mesoporous Silsesquioxane. Chem. Commun. 2002, No. 23,
2902–2903. https://doi.org/10.1039/B209392H.
(31) Pan, A.; Yang, S.; He, L. POSS-Tethered
Fluorinated Diblock Copolymers with Linear- and Star-Shaped Topologies:
Synthesis, Self-Assembled Films and Hydrophobic Applications. RSC Adv. 2015,
5 (68), 55048–55058. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA08619A.
(32) Sanil, E. S.; Cho, K.-H.; Hong, D.-Y.; Lee,
J. S.; Lee, S.-K.; Ryu, S. G.; Lee, H. W.; Chang, J.-S.; Hwang, Y. K. A
Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Functionalized Copper Trimesate. Chem.
Commun. 2015, 51 (40), 8418–8420.
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC01928A.
(33) Wang, X.; Ye, Q.; Song, J.; Cho, C. M.; He,
C.; Xu, J. Fluorinated Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes. RSC Adv. 2014,
5 (6), 4547–4553. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA15108A.
(34) Suenaga, K.; Tanaka, K.; Chujo, Y.
Heat-Resistant Mechanoluminescent Chromism of the Hybrid Molecule Based on
Boron Ketoiminate Modified Octasubstituted Polyhedral Oligomeric
Silsesquioxane. Chem. – Eur. J. 2017, 23 (6), 1409–1414.
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201604662.
(35) Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, H. Water-Soluble
Luminescent Hybrid Composites Consisting of Oligosilsesquioxanes and Lanthanide
Complexes and Their Sensing Ability for Cu2+. Chem. – Eur. J. 2016,
22 (9), 3037–3043. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201504300.
(36) Shen, R.; Feng, S.; Liu, H.
Silsesquioxane-Based Luminescent PMMA Nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2016,
6 (64), 59305–59312. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA10165H.
(37) Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Dang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu,
J.; Fu, J.; Shi, L. Lanthanide Complex-Functionalized Polyhedral Oligomeric
Silsesquioxane with Multicolor Emission Covered from 450 Nm to 1700 Nm. New
J. Chem. 2016, 40 (1), 209–216.
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ02105G.
(38) Yu, T.; Wang, X.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhao,
Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. Synthesis and Photo- and Electro-Luminescent Properties
of Ir(III) Complexes Attached to Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane
Materials. RSC Adv. 2015, 5 (98), 80572–80582.
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA16201G.
(39) Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, T.; Li, H. The
First Europium(III) β-Diketonate Complex Functionalized Polyhedral Oligomeric
Silsesquioxane. Chem. – Eur. J. 2014, 20 (9), 2551–2556.
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201303957.
(40) Zhu, Y. K.; Guang, S. Y.; Su, X. Y.; Xu, H.
Y.; Liu, X. Y. Highly Efficient and Stable Solid-State Luminescent Nanohybrids:
Precise Architecture and Enhancement Mechanism. J. Mater. Res. 2013,
28 (8), 1061–1069. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.36.
(41) Aghajamali, M.; Iqbal, M.; Purkait, T. K.;
Hadidi, L.; Sinelnikov, R.; Veinot, J. G. C. Synthesis and Properties of
Luminescent Silicon Nanocrystal/Silica Aerogel Hybrid Materials. Chem.
Mater. 2016, 28 (11), 3877–3886.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b01114.
(42) Li, Z.; Kong, J.; Wang, F.; He, C.
Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes (POSSs): An Important Building Block for
Organic Optoelectronic Materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5
(22), 5283–5298. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TC01327B.
(43) Zhou, H.; Ye, Q.; Xu, J. Polyhedral
Oligomeric Silsesquioxane-Based Hybrid Materials and Their Applications. Mater
Chem Front 2017, 1 (2), 212–230.
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6QM00062B.
(44) Prateek; Thakur, V. K.; Gupta, R. K. Recent
Progress on Ferroelectric Polymer-Based Nanocomposites for High Energy Density
Capacitors: Synthesis, Dielectric Properties, and Future Aspects. Chem. Rev.
2016, 116 (7), 4260–4317.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00495.
(45) Pan, R.; Wang, L. L.; Shanks, R.; Liu, Y.
The Influence of Trisilanolisobutyl POSS on Domain Microstructure of a
Polyurethane Hybrid Composite: A Molecular Simulation Approach. Silicon 2016,
1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9463-3.
(46) Miyauchi, S.; Imoto, H.; Naka, K.
Fabrication of Polymer-Calcite Composite Thin Films by Phase Transition of
Vaterite Composite Particles with Octacarboxy-Terminated T8-Caged
Silsesquioxane. Polym. J. 2016, 48 (10), 1019–1027.
https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2016.69.
(47) Knauer, K. M.; Jennings, A. R.; Bristol, A.
N.; Iacono, S. T.; Morgan, S. E. Enhanced Surface Properties of Branched
Poly(Ether Sulfone) from Semifluorinated Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsequioxanes. ACS
Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8 (19), 12434–12444.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b01936.
(48) Jiang, B.; Zhang, K.; Cai, Q.; Zeng, T.;
Zhu, M. Effect of Homologous Nano-Composites on the Thermal Degradation of the
Silicone Resin. Soft Mater. 2016, 14 (4), 288–296.
https://doi.org/10.1080/1539445X.2016.1210638.
(49) Czarnecka-Komorowska, D.; Sterzynski, T.;
Dutkiewicz, M. Polyoxymethylene/Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane
Composites: Processing, Crystallization, Morphology and Thermo-Mechanical
Behavior. Int. Polym. Process. 2016, 31 (5), 598–606.
https://doi.org/10.3139/217.3243.
(50) Bele, A.; Dascalu, M.; Tugui, C.; Iacob,
M.; Racles, C.; Sacarescu, L.; Cazacu, M. Dielectric Silicone Elastomers Filled
with in Situ Generated Polar Silsesquioxanes: Preparation, Characterization and
Evaluation of Electromechanical Performance. Mater. Des. 2016, 106,
454–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.06.010.
(51) Tan, H.; Zheng, J.; Xu, D.; Wan, D.; Qiu,
J.; Tang, T. Dependence of Melt Behavior of Star Polystyrene/POSS Composites on
the Molecular Weight of Arm Chains. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118
(19), 5229–5239. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp502946d.
(52) Lin, O. H.; Mohd Ishak, Z. A.; Akil, H. M.
Preparation and Properties of Nanosilica-Filled Polypropylene Composites with
PP-Methyl POSS as Compatibiliser. Mater. Des. 2009, 30
(3), 748–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2008.05.007.
(53) Saparov, B.; Mitzi, D. B. Organic–Inorganic
Perovskites: Structural Versatility for Functional Materials Design. Chem.
Rev. 2016, 116 (7), 4558–4596.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00715.
(54) Kuroda, K.; Shimojima, A.; Kawahara, K.;
Wakabayashi, R.; Tamura, Y.; Asakura, Y.; Kitahara, M. Utilization of
Alkoxysilyl Groups for the Creation of Structurally Controlled Siloxane-Based
Nanomaterials. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26 (1), 211–220.
https://doi.org/10.1021/cm4023387.


Comments
Post a Comment